Introduction
Every NEET, JEE, and board exam aspirant knows that NCERT is the foundation of scoring well. Teachers repeat the same message: “NCERT is enough.” Yet when the exam arrives, most students admit something surprising—they can’t remember NCERT. They read a chapter twice, sometimes five times, and highlight all the important lines but still forget the content during tests.
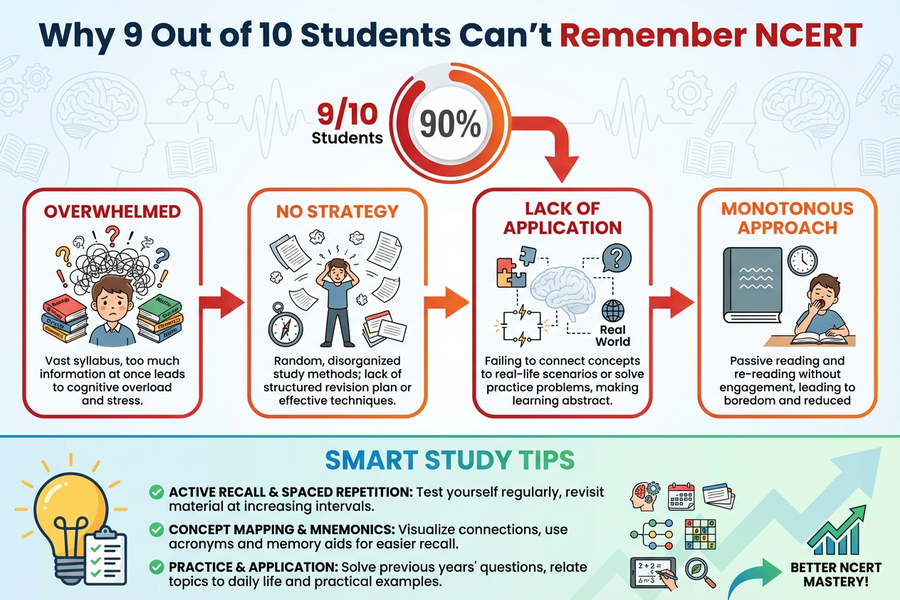
So why does this happen? Why do 9 out of 10 students fail to retain NCERT, even though it is written in simple language?
The answer lies not in the book, but in the study method. Students are reading NCERT incorrectly. They read it passively, revise randomly, try to memorize without understanding, and skip the learning techniques that actually build memory. This blog explains the real reasons behind poor NCERT retention and how students can fix this problem using simple and scientifically proven methods.

The Real Reason Students Forget NCERT
The biggest reason students cannot remember NCERT is because they treat it like any other textbook. But NCERT is not a normal book—every line matters. Even a small sentence can become an exam question. If students read NCERT casually, the brain does not store that information deeply.
Most students simply move their eyes over the text. They don’t question it, they don’t recall it, and they don’t practice it. The brain forgets anything that isn’t processed deeply.
Another major reason is that students read NCERT once and feel confident—but retention requires multiple spaced revisions, not just reading.
Most students fail to remember NCERT because of these combined issues:
-
Passive reading
-
No active recall
-
No spaced repetition
-
Over-highlighting
-
Lack of understanding
-
Zero connection between chapters
-
Distraction while studying
-
Not solving enough questions
-
Studying at the wrong time of day
Let’s understand each one.
Why Students Can’t Remember NCERT: 9 Big Reasons
1. Passive Reading Instead of Active Recall
Most students read NCERT like a storybook. They read line after line without questioning it. Passive reading creates short-term memory—which disappears in hours. Students may feel they “understood” the chapter, but they cannot recall it during a test.
The solution is simple:
After reading a paragraph, close the book and try to explain it in your own words. This builds long-term memory.
2. No Proper Revision Schedule
Research on the forgetting curve shows that humans forget 70% of new information within 24 hours if they don’t revise. Students read NCERT once and assume they will remember it during exams. That is impossible.
An effective revision cycle is
Day 1 → Day 3 → Day 7 → Day 21 → Day 45
This spaced approach moves information into long-term storage.
3. Highlighting Too Much Content
Students love highlighting. Some highlight so much that the entire book becomes yellow or blue. Highlighting feels productive, but it does not improve memory. Too many highlights reduce clarity.
Highlight only:
-
Definitions
-
NCERT keywords
-
Important one-liners
-
Tables and examples
Less highlighting = better clarity.
4. Memorising Without Understanding
Many students try to memorise NCERT lines without understanding the concept. Rote learning works for a day but collapses during an exam. NCERT lines stick only when you understand the meaning behind them.
Students should ask:
-
Why is this line important?
-
What does this concept explain?
-
How is this related to the next topic?
Understanding leads to strong recall.
5. Not Practicing Questions After Reading
NCERT is theory, but exams test application. Students who only read NCERT forget it quickly because they never test their recall.
After every chapter, solving 50–100 MCQs helps the brain recognize patterns. Every wrong answer is an opportunity to recheck NCERT and strengthen memory.
6. Ignoring Diagrams, Tables and Flowcharts
NCERT diagrams are extremely important. In biology especially, visual memory is stronger than verbal memory. Students who skip diagrams lose a powerful learning tool.
Redrawing diagrams, labeling them from memory, and revising them weekly significantly improves retention.
7. Studying When the Brain Is Tired
Many students read NCERT late at night when the brain is exhausted. During this time, the brain cannot form strong memories. Learning requires alertness.
The best time to study NCERT is
-
Early morning
-
After a short break
-
When the mind is fresh
This boosts comprehension and retention.
8. Multitasking and Distractions
Students try to study with their phone next to them. Even small notifications break concentration. Switching between apps, music, or messages resets attention and weakens memory.
For strong NCERT recall:
-
Keep the phone in another room
-
Study in focused blocks
-
Avoid switching between subjects
A distraction-free environment improves learning.
9. No Testing-Based Revision
Many students avoid tests because they fear scoring low. But tests are the strongest way to remember NCERT. When you take a test, your brain retrieves information, strengthening memory pathways.
Weekly subject tests and monthly full tests ensure that NCERT content remains in the brain for long.
How Students Can Finally Remember NCERT (Proven Strategies)
Once you understand why you forget NCERT, fixing it becomes much easier. Here are powerful methods that help students retain NCERT effortlessly:
1. Read NCERT Slowly and Carefully
Do not rush. Read every line with attention. Try turning each paragraph into a 1–2 line summary in your own words.
2. Use Active Recall Every Day
Close the book and try to explain the topic aloud or write it down from memory. This forces the brain to store information deeply.
3. Follow Spaced Revision
Repeat the chapter after 1 day, 3 days, 7 days, and 21 days. This prevents forgetting completely.
4. Create Minimal Notes
Write only essential NCERT points. Do not rewrite entire paragraphs. The goal is clarity, not volume.
5. Practice 50–100 Questions After Each Chapter
This connects understanding with application.
6. Pay Attention to Diagrams and Tables
Redraw diagrams and revise them frequently.
7. Take Regular Tests
Chapter tests, mini tests, and full syllabus tests build strong recall.
8. Avoid Studying When Tired
Your brain needs energy to store information. Study when you are mentally fresh.
9. Keep Distractions Away
Airplane mode, silent mode, or studying without a phone helps you remember much better.
Conclusion
Students forget NCERT not because NCERT is difficult, but because their study method is ineffective. Passive reading, over-highlighting, lack of revision, skipping diagrams, and avoiding tests are the primary reasons why 9 out of 10 students can’t remember NCERT.
However, with the right approach—active recall, spaced revision, question practice, focused reading, and consistent testing—NCERT becomes easy to remember. Once students master NCERT, exams like NEET, JEE, and CBSE Boards become far more manageable.
The key to remembering NCERT is simple:
Don’t read more. Read better.
Also Read: NEET Anxiety Tips: How to Stay Calm and Mentally Strong