Psychology of Thumbnails and Titles — Why People Click
In today’s digital world, the psychology of thumbnails and titles plays a massive role in what people choose to click. Every day, users scroll through hundreds of images, posts, videos, and articles. Yet only a few pieces capture attention. This behaviour is not random. It is driven by how the human brain reacts to visuals, emotions, patterns, colours, and curiosity. Understanding the psychology behind thumbnails and titles helps creators design content that stands out and pulls people in.
People click because their attention is captured, their curiosity is activated, or their emotions are triggered. A thumbnail creates the first impression, and a title completes the spark. Together, they influence decision-making within seconds. If creators understand this psychology deeply, they can dramatically increase their engagement and visibility.
How the Psychology of Thumbnails and Titles Captures Attention
The human brain filters massive amounts of information every second. It only stops when something breaks the pattern. This is why the psychology of thumbnails and titles begins with attention. When a thumbnail includes strong contrast, emotion, or a clear focal point, the brain pauses. This pause becomes the moment where clicking becomes possible.
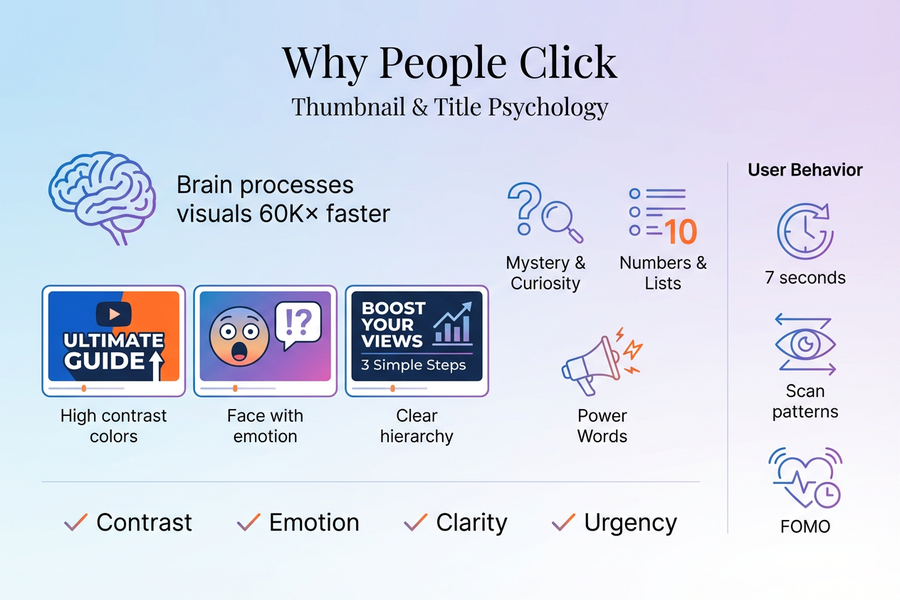
Thumbnails with bright colours, expressive faces, and simple layouts attract the eye faster. People respond to visuals 60,000 times faster than text. Therefore, visuals create the first gateway to the click. Titles are then followed by giving context and direction. Both must work together to catch attention and guide the viewer.
When a thumbnail interrupts normal scrolling behaviour, the mind becomes curious. Curiosity leads to engagement, and engagement leads to clicks.
According to MIT research, the human brain processes visual information in as little as 13 milliseconds.
Curiosity, Emotion, and Trust Drive Click Behaviour
Curiosity is one of the strongest motivators for human action. Titles that create an information gap make people want to know more. Phrases like “The truth behind…” or “You won’t believe…” activate the brain’s reward system. The viewer feels a small tension that can only be resolved by clicking.
Emotion also plays a huge role. People click when they feel something: surprise, excitement, fear, joy, or even confusion. Emotional faces in thumbnails increase click-through rates because humans instinctively respond to expressions. A thumbnail showing shock or amazement triggers instant interest.
Trust is another key factor in the psychology of thumbnails and titles. People do not click content that looks fake, confusing, or misleading. Clean design, honest messaging, and a consistent style help build credibility. When viewers trust a creator, they click more often and more confidently.
Why Pattern Breaks Make People Click
The brain loves patterns, but it also notices when a pattern is broken. Most scrolling is repetitive. People scroll without thinking. But when a thumbnail breaks the visual flow, the brain switches to attention mode. This sudden change makes the viewer stop, observe, and respond.
Pattern breaking works through:
• unusual visuals
• unexpected colours
• surprising expressions
• bold text placement
• contrasting elements
Titles can also break patterns. For example:
• “The mistake every expert makes”
• “Why success depends on doing less”
These create mental friction. The viewer wants the answer, so they click.
Clarity Is More Powerful Than Creativity
Clarity is one of the strongest psychological principles in digital design. People click when they understand quickly. Confusing thumbnails or vague titles increase cognitive load. When the brain works too hard, the viewer skips the content.
The best titles clearly explain:
• what the content is about
• why someone should care
• how it will help or surprise them
Thumbnails should also be clean, simple, and focused. One subject, one emotion, one message.
In the psychology of thumbnails and titles, clarity builds confidence, and confidence creates clicks.
Faces, Emotions, and Human Connection Improve Clicks
Humans are drawn to faces more than any other visual element. A thumbnail showing a face creates an instant connection. The viewer tries to interpret the emotion. This triggers curiosity. Even a slight expression of confusion or excitement can increase engagement.
Emotional faces work because they activate the mirror neurone system. The viewer feels the emotion shown in the image. This emotional reaction creates an instant desire to know more. Titles amplify this emotion by explaining what the viewer can expect.
Identity and Relevance Increase Clicking Behaviour
People click when content feels relevant to them personally. This is where identity comes in. When a title calls out a specific group, the brain filters it as “for me”. For example:
• “For new digital marketers…”
• “For students learning AI…”
• “For business owners…”
Relevance reduces mental effort. People click faster when they believe the content will meet their needs.
Numbers and Lists Improve Clarity and Predictability
Titles with numbers perform better because they create structure. The viewer knows exactly what to expect:
• 5 tips
• 7 mistakes
• 10 secrets
Lists reduce uncertainty. This is comforting to the brain. Predictability encourages action. The psychology behind list-based titles is simple: organised content feels easier to consume, so people click more.
Fear of Missing Out Influences Clicks
FOMO, or fear of missing out, is a powerful clicking trigger. People click when they feel they might miss something valuable or time-sensitive. Phrases like:
• “Don’t miss this…”
• “Before you do this…”
• “The trend everyone is ignoring…”
Create urgency. Urgency activates the survival part of the brain. Clicking becomes the fastest way to remove uncertainty.
Colour Contrast and Visual Design Shape Click Behaviour
Colour affects emotion. Certain colours trigger strong reactions:
• Red → urgency
• Yellow → excitement
• Blue → trust
• Green → calm
• Black → power
High contrast makes thumbnails stand out. The brain notices contrast quickly. This helps content rise above competing visuals. Good design increases the chances of capturing attention and converting it into a click.
Thumbnails and Titles Must Match
A mismatch between thumbnail and title creates confusion. Confusion kills curiosity. For clicking to happen, the brain needs consistency. The thumbnail must hint at the story, and the title must reinforce that hint.
When both elements match, the viewer feels confident that clicking will give them value. When they mismatch, the brain rejects the content.
Harmony leads to clicks.
Conclusion: Clicking Is a Psychological Reaction
People click because thumbnails attract them and titles convince them. Clicking is not random—it is a psychological decision. By understanding the psychology of thumbnails and titles, creators can design content that stands out and compels action.
Emotions trigger curiosity.
Clarity builds trust.
Pattern breaks capture attention.
Consistency drives interest.
Relevance guides behaviour.
When creators master these principles, their content becomes far more impactful. Thumbnails start conversations. Titles finish them. Together, they determine whether someone scrolls past—or stops and clicks.
Also Read: SEO in 2025: What Actually Works Now for Real Results