Remember that science project where you placed a plant near the window and another in a dark cupboard? Within days, the plant by the window looked vibrant and green, while the one in darkness turned pale and weak. That simple experiment revealed one of nature’s most beautiful secrets photosynthesis.
Every breath you take, every meal you eat, and almost every living thing on Earth depends on this incredible process. For students preparing for exams or simply curious about how life works, understanding photosynthesis isn’t just about scoring marks it’s about understanding the very foundation of life on our planet.
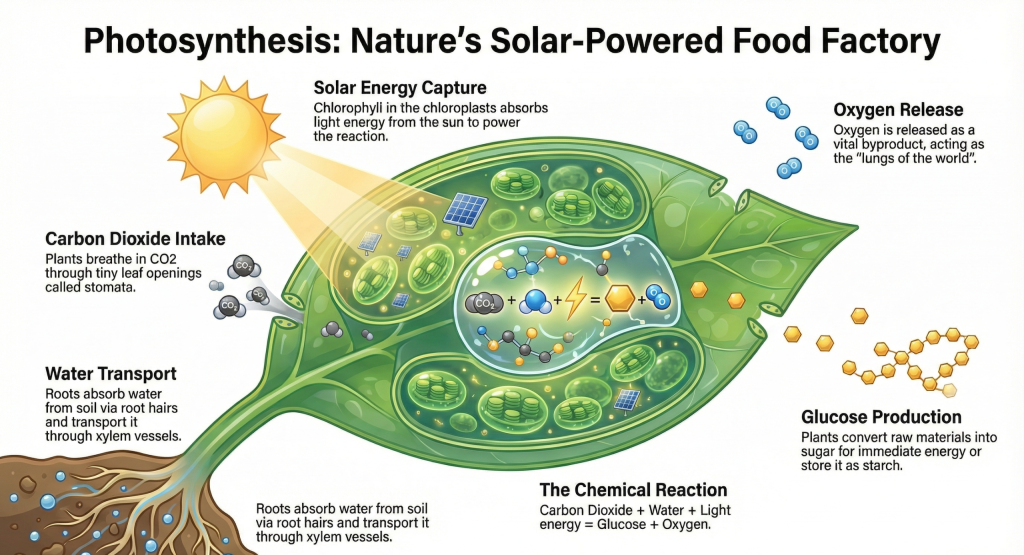
What is Photosynthesis?
Photosynthesis is nature’s way of making food. It’s the process through which green plants, algae, and some bacteria convert light energy (usually from the sun) into chemical energy stored in glucose (sugar).
Think of plants as tiny food factories. They take in carbon dioxide from the air, water from the soil, and energy from sunlight, then magically transform these ingredients into food for themselves and oxygen for us to breathe.
The word photosynthesis comes from two Greek words: photo meaning light, and “synthesis” meaning putting together. So literally, it means “putting together with light.”
Photosynthesis Definition and Meaning
Definition: Photosynthesis is the process by which plants make their own food using sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide, while releasing oxygen as a by-product.
Academic Definition: Photosynthesis is a biochemical process in which autotrophic organisms convert light energy into chemical energy, producing carbohydrates from carbon dioxide and water in the presence of chlorophyll.
Photosynthesis Meaning in Hindi: प्रकाश संश्लेषण (Prakash Sanshleshan) – यह वह प्रक्रिया है जिसमें पौधे सूर्य के प्रकाश, पानी और कार्बन डाइऑक्साइड का उपयोग करके अपना भोजन बनाते हैं।
The Photosynthesis Equation and Formula
Understanding the photosynthesis formula is crucial for exams from Class 6 onwards.
Simple Word Equation:
Carbon Dioxide + Water + Light Energy → Glucose + Oxygen
Chemical Equation (Photosynthesis Formula):
6CO₂ + 6H₂O + Light Energy → C₆H₁₂O₆ + 6O₂
Breaking it down:
- 6CO₂ = Six molecules of carbon dioxide
- 6H₂O = Six molecules of water
- Light Energy = Usually from sunlight
- C₆H₁₂O₆ = One molecule of glucose (sugar)
- 6O₂ = Six molecules of oxygen
Memory Trick: Remember “6-6-1-6” for the numbers in the equation.
How Does Photosynthesis Work? The Complete Process
Photosynthesis happens primarily in the leaves of plants, specifically in tiny structures called chloroplasts. These contain a green pigment called chlorophyll that captures light energy.
The Basic Process:
Stage 1: Light Reactions (Light-Dependent)
- Occur in the thylakoid membranes inside chloroplasts
- Chlorophyll absorbs sunlight
- Water molecules split (photolysis)
- Oxygen is released
- Energy is captured in molecules called ATP and NADPH
Stage 2: Dark Reactions or Calvin Cycle (Light-Independent)
- Occur in the stroma of chloroplasts
- Don’t need direct light but use energy from light reactions
- Carbon dioxide is fixed into glucose
- The cycle continues producing sugar
Think of it like a restaurant kitchen: the light reactions are like receiving and preparing raw ingredients, while the Calvin cycle is like cooking the actual meal.
Understanding the Photosynthesis Reaction
The photosynthesis reaction is an endergonic process, meaning it requires energy input (from sunlight) to proceed.
Components of the Reaction:
Reactants (What Goes In):
- Carbon dioxide (from air through stomata)
- Water (from roots through xylem)
- Light energy (absorbed by chlorophyll)
Products (What Comes Out):
- Glucose (stored energy for the plant)
- Oxygen (released through stomata)
Location: Primarily in leaf mesophyll cells containing chloroplasts.
Catalyst: Chlorophyll acts as the essential catalyst that makes this reaction possible.
The 7 Steps of Photosynthesis Explained
- Step 1: Absorption of Light Chlorophyll in the leaves absorbs sunlight, particularly red and blue wavelengths.
- Step 2: Splitting of Water (Photolysis) Light energy splits water molecules into hydrogen and oxygen. Oxygen is released into the air.
- Step 3: Energy Conversion Light energy converts into chemical energy stored in ATP and NADPH molecules.
- Step 4: Carbon Fixation Carbon dioxide from air enters through stomata and gets fixed by an enzyme called RuBisCO.
- Step 5: Reduction ATP and NADPH from light reactions reduce carbon compounds to form simple sugars.
- Step 6: Regeneration Some of the sugar molecules are used to regenerate the cycle’s starting compounds.
- Step 7: Glucose Formation Simple sugars combine to form glucose, which plants use for energy and growth.
Photosynthesis Diagram: Visual Understanding
While we can’t show actual diagrams here, here’s how to draw and label a photosynthesis diagram for your exams:
Essential Elements to Include:
Leaf Cross-Section:
- Upper epidermis
- Palisade mesophyll (where most photosynthesis occurs)
- Spongy mesophyll
- Lower epidermis with stomata
- Chloroplasts (shown as green structures)
Arrows Showing:
- Sunlight entering from top
- CO₂ entering through stomata
- Water moving up from roots
- Oxygen exiting through stomata
- Glucose being produced
Label: Chloroplast detail showing thylakoids and stroma
Which Bacteria Can Perform Photosynthesis?
Not all photosynthesis happens in plants. Several bacteria can also perform this amazing process, making them crucial for Earth’s ecosystems.
Photosynthetic Bacteria Include:
Cyanobacteria (Blue-Green Algae)
- Perform oxygenic photosynthesis (release oxygen)
- Found in water bodies
- Example: Nostoc, Anabaena
Purple Bacteria
- Perform anoxygenic photosynthesis (don’t release oxygen)
- Use hydrogen sulfide instead of water
- Example: Chromatium, Rhodospirillum
Green Sulfur Bacteria
- Also anoxygenic
- Found in deep water with low light
- Example: Chlorobium
Purple Non-Sulfur Bacteria
- Very versatile, can switch between photosynthesis and other energy sources
- Example: Rhodopseudomonas
These bacteria were Earth’s first photosynthesizers, producing oxygen billions of years ago that made our atmosphere breathable.
Why is Photosynthesis Important?
- Produces Oxygen Every breath you take contains oxygen produced by photosynthesis. About 70% comes from ocean algae and phytoplankton.
- Creates Food All food chains start with photosynthesis. Even when you eat chicken, that chicken ate grain produced through photosynthesis.
- Removes Carbon Dioxide Plants act as Earth’s air purifiers, removing CO₂ that would otherwise trap heat and warm the planet.
- Provides Energy Fossil fuels (coal, oil, natural gas) come from ancient plants that used photosynthesis millions of years ago.
- Maintains Balance Photosynthesis balances cellular respiration, creating a perfect oxygen-carbon dioxide cycle.
Real-Life Examples of Photosynthesis
- Example 1: Your School Garden The tulsi or money plant in your classroom produces oxygen during the day while absorbing CO₂.
- Example 2: Rice and Wheat Fields The crops growing in fields use photosynthesis to create the grains we eat as rice and chapatis.
- Example 3: Forest Ecosystems The Amazon rainforest, called “Earth’s lungs,” produces about 20% of our planet’s oxygen through photosynthesis.
- Example 4: Aquatic Plants Water plants in aquariums and ponds perform underwater photosynthesis, providing oxygen for fish.
- Example 5: Succulents and Cacti Desert plants have adapted photosynthesis to work with minimal water, opening stomata only at night.
Common Mistakes Students Make
- Mistake 1: Thinking photosynthesis happens only in leaves any green part of a plant (young stems, unripe fruits) can photosynthesize.
- Mistake 2: Confusing respiration with photosynthesis makes food using CO₂; respiration breaks down food releasing CO₂. They’re opposites.
- Mistake 3: Believing plants don’t respire plants both photosynthesize (during day) and respire (all the time).
- Mistake 4: Writing incorrect chemical formulas always balance the equation: 6CO₂ + 6H₂O → C₆H₁₂O₆ + 6O₂
- Mistake 5: Saying chlorophyll is food chlorophyll is the tool that captures light; glucose is the food produced.
Easy Tips to Remember Photosynthesis
Acronym for Requirements:CWLS
- C = Carbon dioxide
- W = Water
- L = Light
- S = Special chlorophyll
Rhyme to Remember: “Plants breathe in CO₂, water from the ground they drew, add some sunlight bright and true, out comes oxygen and food for you!”
Hand Trick:
- Left hand = Reactants (CO₂, Water, Light)
- Right hand = Products (Glucose, Oxygen)
- Clap = The reaction happens
FAQs About Photosynthesis
Q. What is photosynthesis in short answer?
Photosynthesis is the process where plants use sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide to create their own food (glucose) and release oxygen. It’s how plants make energy to grow and survive.
Q. What is the photosynthesis formula?
The photosynthesis formula is 6CO₂ + 6H₂O + Light Energy → C₆H₁₂O₆ + 6O₂. This means six carbon dioxide molecules plus six water molecules plus light energy produce one glucose molecule and six oxygen molecules.
Q. What is the process of photosynthesis?
Photosynthesis involves two main stages: light reactions where chlorophyll absorbs sunlight and splits water molecules, and the Calvin cycle where carbon dioxide is converted into glucose using the energy captured from light reactions.
Q. What is photosynthesis for class 3?
For younger students, photosynthesis is simply how plants make their food using sunlight, air, and water. Just like we need food to grow, plants make their own food using these three things and sunlight.
Q. What are the 7 steps to photosynthesis?
The seven steps are: light absorption by chlorophyll, water splitting, energy conversion to ATP and NADPH, carbon dioxide fixation, reduction of carbon compounds, regeneration of cycle molecules, and finally glucose formation.
Q. Why is photosynthesis important?
Photosynthesis is important because it produces the oxygen we breathe, creates food for nearly all living things, removes carbon dioxide from the atmosphere, and maintains Earth’s ecological balance. Without it, life as we know it wouldn’t exist.
Q. What are 5 examples of photosynthesis?
Five examples include: trees in forests producing oxygen, crops like rice and wheat growing in fields, algae in oceans creating marine food chains, houseplants purifying indoor air, and desert cacti making food with minimal water.
Q. Which of the following bacteria can perform photosynthesis?
Cyanobacteria (blue-green algae), purple bacteria, green sulfur bacteria, and purple non-sulfur bacteria can perform photosynthesis. Cyanobacteria release oxygen like plants, while others perform anoxygenic photosynthesis without releasing oxygen.
Conclusion
Photosynthesis isn’t just another chapter to memorize for your science exam it’s the foundation of life on Earth. Every time you see a green leaf, remember that it’s a tiny factory working tirelessly to feed the planet and keep our air breathable.
For students, mastering photosynthesis helps you understand biology, ecology, and environmental science at deeper levels. The equation, the process, and the importance of this reaction will appear in exams from middle school through college, making it one of the most valuable concepts to grasp.

