If you are studying Biology and wondering about the meaning of turgid in biology, you are not alone. This word often appears in NCERT chapters related to plant cells, osmosis, and cell structure, especially in Classes 9 and 10.
Simply put, what is turgid refers to the condition of a plant cell when it becomes swollen due to water entering it. Understanding this term is important for exams, as it helps students explain how plant cells stay firm and upright. Parents may also notice this concept linked to basic plant growth and health taught in school Biology.
What Is the Meaning of Turgid in Biology?
Simple Explanation for Students
The meaning of turgid in biology refers to the state of a plant cell when it becomes full of water and feels firm or swollen. This happens when water enters the cell through a natural process called osmosis.
In simple words, turgidity meaning is the pressure created inside a plant cell after it absorbs water. Because of this pressure, the cell wall stays tight, and the plant looks fresh and upright.
One-line exam-ready definition:
A cell is called turgid when it gains water and becomes firm due to internal pressure against the cell wall.
For students, this concept is important in understanding how plants stand straight without bones. For parents, it explains a basic life process that children learn in school Biology.
What Does It Mean When a Cell Is Turgid?
When students ask what does it mean when a cell is turgid, it simply means that the cell has absorbed enough water and has become firm and swollen. This condition is commonly seen in healthy plant cells.
A turgid cell looks full and strong because the water inside pushes against the cell wall. This pressure helps plants keep their shape and prevents them from wilting, which is why well-watered plants stand straight.
Why Does a Cell Become Turgid?
A cell becomes turgid due to a natural process called osmosis. Water moves from an area where it is more available to an area where it is less available, and enters the cell.
Inside the plant cell, the large vacuole stores this water. As the vacuole fills up, it presses against the cell wall, making the cell firm. This strong cell wall prevents the cell from bursting, which is an important point students often need to remember for exams.
Example of a Turgid Cell (Easy to Understand)
Simple School-Level Example
A common turgid cell example that students learn in school is a fresh green leaf. When a leaf has enough water, its cells are filled and firm, so the leaf looks healthy and upright.
Another easy example is a potato strip experiment done in school labs. When a potato strip is kept in plain water, it absorbs water and becomes stiff. This shows the turgid meaning in botany, where plant cells gain water and become firm.
These examples help students connect textbook terms with real life. For parents, such experiments show how basic Biology concepts are taught practically in school to improve understanding, not just memorisation.
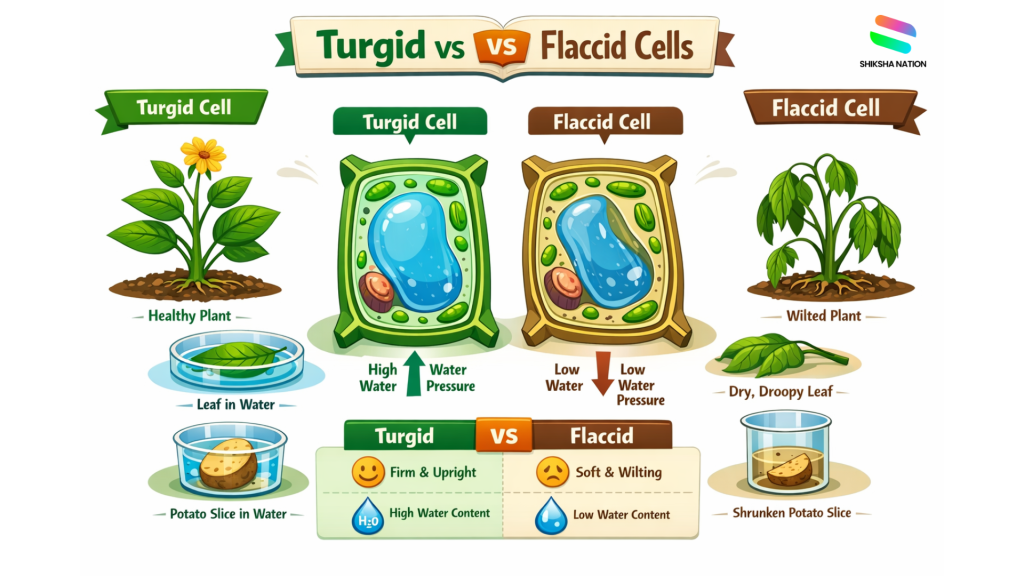
Difference Between Turgid and Flaccid Cells
Understanding the turgid and flaccid meaning in biology is very important for school exams. Students are often asked to compare these two conditions to show how water affects plant cells. Simply put, a flaccid cell is the opposite of turgid biology.
Turgid Cell
A turgid cell is a healthy plant cell that has absorbed enough water. The cell becomes firm and strong, helping the plant stay upright and fresh. This condition shows proper water balance in plants.
Flaccid Cell
A flaccid cell is a plant cell that has lost water. Because of less water inside, the cell becomes soft and weak. Plants with many flaccid cells start drooping or wilting, which students often observe in dry conditions.
Comparison Table: Turgid vs Flaccid Cells
| Point of Difference | Turgid Cell | Flaccid Cell |
| Water content | High water inside the cell | Low water inside the cell |
| Cell condition | Firm and swollen | Soft and loose |
| Plant appearance | Fresh and upright | Wilted or drooping |
| Cell pressure | High internal pressure | Low internal pressure |
| Exam importance | Shows healthy cell state | Shows lack of water |
For parents, this comparison explains why regular watering is important for plants. For students, this table is useful for quick revision before exams.
Where Is “Turgid” Asked in CBSE Exams?
The term turgid is commonly asked in CBSE Biology because it is linked to basic plant cell functions. Knowing the meaning of turgid in biology class 9 helps students answer questions confidently and score easy marks.
Class 9: Cell Structure and Osmosis
In Class 9 NCERT, turgid appears in the chapter related to cell structure and movement of substances. Students are expected to explain how water enters a plant cell and makes it firm.
Questions are usually simple, such as:
- What is a turgid cell?
- Why does a plant cell become turgid?
These are often 1-mark or 2-mark questions.
Class 10: Life Processes and Transport
In Class 10, the concept may come indirectly while studying life processes. Students might need to explain the role of water in plants or relate turgidity to healthy plant cells.
Here, questions may ask for:
- Short explanations
- Differences between cell conditions
Class 11: Plant Physiology Basics
In Class 11 Biology, turgidity is connected to plant water balance and cell pressure. Questions become slightly more detailed but still focus on understanding, not memorisation.
Students may see:
- Explain the importance of turgidity in plants
- How does turgidity help plants remain upright?
For parents, this shows why children keep learning the same concept at different levels. For students, mastering this topic early makes higher classes easier and reduces exam stress.
Common Student Confusion: Turgidity vs Rigidity
Many students get confused between turgidity and rigidity because both words suggest firmness. However, in Biology, these terms are not the same and should not be mixed, especially in exams.
Understanding the Difference Clearly
Turgidity is related to water inside a plant cell. When a cell absorbs water, it becomes firm due to internal pressure. This firmness is temporary and depends on water availability.
On the other hand, rigidity meaning in biology refers to the stiffness of a structure due to its material or build, not because of water movement. It is not a core plant cell process like turgidity.
For students, remembering this difference helps avoid wrong answers in exams. For parents, this confusion is common and part of learning, which is why clear explanations in school Biology are important.
Turgid in Biology (FAQ)
Is a turgid cell alive or dead?
A turgid cell is alive. It becomes turgid only when normal life processes like water absorption are working properly. Dead cells cannot take in water in this way.
Can animal cells become turgid?
No, animal cells do not become turgid. They do not have a strong cell wall like plant cells. This is why the idea of what is turgid is mainly used for plant cells in Biology.
Is turgidity good for plants?
Yes, turgidity is very important for plants. It helps plants stay upright, keeps leaves fresh, and supports normal growth. Without turgidity, plants start wilting.
What happens when a turgid cell loses water?
When a turgid cell loses water, it becomes soft and loose. This change shows that water balance in the cell is disturbed, which students often see in dry plants.
Where do students mostly get confused about turgid cells?
Students often confuse turgid cells with flaccid cells or mix them with other terms. Clear understanding of turgid meaning in biology helps avoid such mistakes in exams.
Is “turgid” important for exams?
Yes, turgid is an important term for CBSE exams. It is commonly asked in 1–2 mark questions, definitions, and short explanations, especially in plant-related chapters.

