What Is the Lens Formula?
A lens formula is a mathematical relationship that connects:
- Object distance (u)
- Image distance (v)
- Focal length (f)
It helps determine the position, size, and nature of images formed by convex and concave lenses. These formulas are fundamental in optics, used in spectacles, cameras, microscopes, and telescopes.
Complete Lens Formula Table (With Explanations)
Sign Convention (Must Know)
- Distances measured in the direction of incident light → positive
- Distances measured opposite to incident light → negative
- Convex lens focal length → positive
- Concave lens focal length → negative
Core Lens Formulas
| Formula Name | Formula | Explanation | Applicable Class |
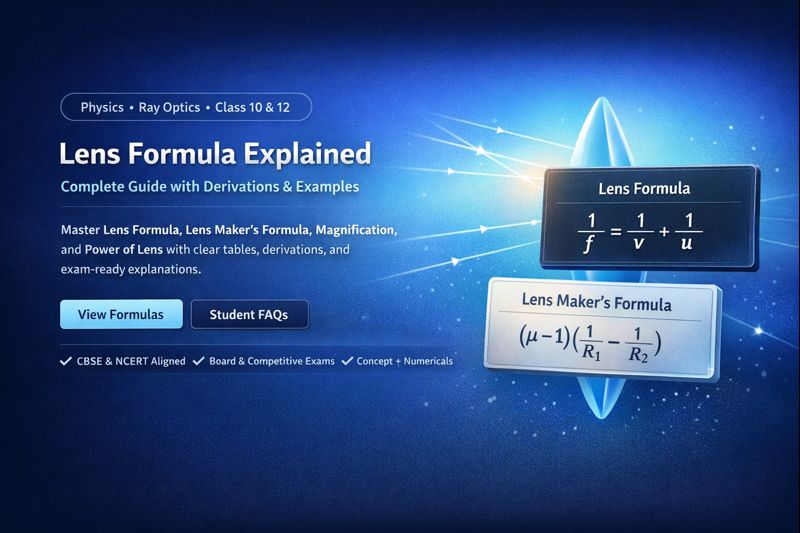
| Lens Formula | 1/f = 1/v + 1/u | Relates focal length, image distance, and object distance for thin lenses | Class 10 |
| Convex Lens Formula | 1/f = 1/v + 1/u | Same formula; f is positive | Class 10 |
| Concave Lens Formula | 1/f = 1/v + 1/u | Same formula; f is negative | Class 10 |
| Magnification (Lens) | m = h₂/h₁ = v/u | Ratio of image height to object height | Class 10 |
| Power of Lens | P = 1/f (f in meters) | Ability of lens to converge/diverge light | Class 10 |
| Unit of Power | Dioptre (D) | 1 D = 1 m⁻¹ | Class 10 |
| Focal Length of Lens | f = 1/P | Inverse of power | Class 10 |
| Mirror Formula (Comparison) | 1/f = 1/v + 1/u | Same mathematical form as lens formula | Class 10 |
Lens Maker’s Formula (Class 12)
| Formula Name | Formula | Explanation | Class Level |
| Lens Maker Formula | 1/f = (μ − 1)(1/R₁ − 1/R₂) | Relates focal length with refractive index and curvature | Class 12 |
| Where | μ = refractive index | R₁, R₂ = radii of curvature | — |
| Lens in Air | μ = μ_lens / μ_air | Usually μ_air ≈ 1 | Class 12 |
| Convex Lens (Lens Maker) | R₁ > 0, R₂ < 0 | Produces converging effect | Class 12 |
| Concave Lens (Lens Maker) | R₁ < 0, R₂ > 0 | Produces diverging effect | Class 12 |
Lens Maker Formula Derivation (Class 12 – Simplified)
Step-by-Step Idea:
- Refraction at first spherical surface
- Refraction at second spherical surface
- Combine both equations
- Apply thin lens approximation
Final Derived Formula:
1/f = (μ−1)(1/R1−2/R2)
- Assumes lens is thin
Medium outside lens is air
What Is Lens Maker’s Formula?
The lens maker’s formula helps optical engineers design lenses by determining how curvature and material affect focal length. It explains why lenses made of different materials behave differently, even if their shapes are similar.
Lens Formula in Excel (Educational Use)
| Parameter | Excel Formula |
| Image Distance (v) | =1/(1/f – 1/u) |
| Focal Length (f) | =1/(1/v + 1/u) |
| Power of Lens | =1/f |
Useful for numerical simulations and school projects
Convex vs Concave Lens
| Feature | Convex Lens | Concave Lens |
| Nature | Converging | Diverging |
| Focal Length | Positive | Negative |
| Image | Real/Virtual | Always Virtual |
| Use | Camera, Eye | Spectacles (myopia) |
FAQs about Lens Formula
Q. What is the lens formula?
The lens formula is 1/f = 1/v + 1/u, relating focal length, image distance, and object distance.
Q. What is lens maker’s formula?
It is 1/f = (μ − 1)(1/R₁ − 1/R₂) and explains how lens shape and material affect focal length.
Q. Is lens formula same for convex and concave lenses?
Yes, but sign conventions differ.
Q. What is the magnification formula for lens?
m = v/u = h₂/h₁
Q. What is the power of lens formula?
P = 1/f (f in meters)
Q. Which class studies lens formula?
Lens formula is taught in Class 10, while lens maker formula is in Class 12.
Q. Why is lens maker formula important?
It helps in designing lenses for optical instruments.
Q. Can lens formula be used for mirrors?
Mathematically yes, but physically mirrors and lenses differ.
Q. What is the SI unit of lens power?
Dioptre (D)
Q. What happens if focal length is negative?
The lens is concave and diverges light.


